NFC in 2022: Improved User Experience, Wireless Charging, Tag Evolution, and Technology Collaboration
 By Andrew Zignani |
07 Jan 2022 |
IN-6402
By Andrew Zignani |
07 Jan 2022 |
IN-6402

Log In to unlock this content.
You have x unlocks remaining.
This content falls outside of your subscription, but you may view up to five pieces of premium content outside of your subscription each month
You have x unlocks remaining.
 By Andrew Zignani |
07 Jan 2022 |
IN-6402
By Andrew Zignani |
07 Jan 2022 |
IN-6402

NFC Continues to Evolve |
NEWS |
The Near-Field Communication (NFC) market has grown considerably over the last decade, driven primarily by the evolution of the mobile contactless payment ecosystem and integration of the technology within smartphones, smartwatches, Point of Sale (POS) terminals, and a number of other reader devices including games consoles, Personal Computers (PCs), and vehicles. In 2021, shipments of NFC-enabled devices exceeded one billion units for the first time and the market is expected to continue growing over the next decade, reaching over 1.6 billion devices by 2026. This will be driven by new features and functionalities enabled by the technology, greater awareness of NFC and contactless technology in the post-COVID-19 world, new use cases, and improvements to the technology and its overall user experience.
2022 Will be a Key Year for NFC's Continued Innovation |
IMPACT |
Over the last couple of years, NFC has introduced a number of new features and enhancements that will enable it to better service its target markets. Key among these include the following:
Wireless Charging: In May 2020, the NFC Forum approved and adopted its first iteration of the Wireless Charging Specification (WLC). This specification enables NFC-enabled devices such as smartphones to utilize the NFC technology for both communications and wireless charging capabilities, making it possible to charge smaller battery-powered consumer and Internet of Things (IoT) devices including audio devices, peripherals, medical devices, and wearables, among others. For example, Bluetooth earbuds that leverage NFC for pairing could also leverage NFC technology to charge the device, avoiding the need for more bulky charging solutions. This is designed as a complementary to solutions such as Qi charging which are more suited to devices that require more power and faster charging. Instead, NFC wireless charging is an intuitive solution designed for smaller products (up to one Watt) without the need to bring a dedicated charger. In October 2021, the NFC Forum approved the WLC 2.0 standard, supporting smaller antenna sizes to make it more viable to allow smaller products to take advantage of these capabilities. A number of NFC solution providers are developing wireless charging capabilities. ABI Research expects the first of these devices to arrive in 2022 as the NFC wireless charging ecosystem develops.
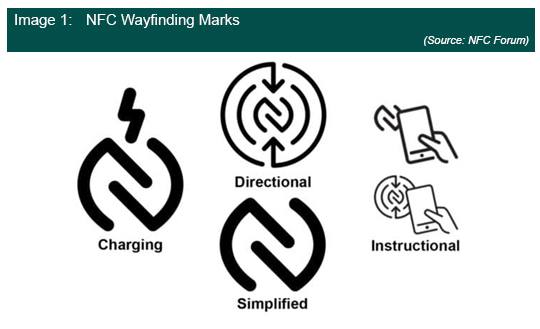
NFC Wayfinding Mark: In November 2021, the NFC Forum introduced several new global identifier graphics to help improve the end user experience and awareness of how and when to use NFC technology. Thanks to NFC’s ability to address a number of different use cases, it has been deployed in a number of different device types. However, one continual problem plaguing NFC is awareness of where to tap on a device in order to interact with it effectively. As the image below demonstrates, the wayfinding marks come in several different formats. The charging mark demonstrates that a device has NFC charging functionality and that this is where the device needing power should be placed. The directional mark is designed predominantly for tag devices and occasionally used devices where there is a need to guide the user to the precise location of the antenna for an improved user experience. The instructional marker are complementary marks that are aimed at markets where NFC familiarity may be lower, providing direct guidance on how to use the technology. The simplified marker is designed for markets where there is greater familiarity and where NFC usage is likely to be more regular.
NFC Tag Improvements and Market Growth: The NFC tag market is forecasted to grow considerably over the next few years as more and more devices adopt the technology for a combination of supply chain monitoring, end user engagement, and authentication and anti-counterfeiting applications. Billions of consumer, medical, IoT, and other products are expected to ship annually from next year onwards. Falling tag costs, improved user experience, new features, improved performance, improved iOS NFC related capabilities, alongside widespread NFC reader penetration and the emergence of feature-rich NFC tags, as well as innovations in silicon tag production efficiency are combining together to enable widespread deployment of NFC tags for marketing, engagement, and brand protection purposes. NFC solution providers have made enormous strides over the last few years to reduce the overall cost of adopting this technology.
Apple recently revealed that it would be adding support for Near-Field Communications tags and stickers that are capable of initiating Apple Pay payments. This can be achieved without the need to download a third-party app for payments, meaning that an end user can simply tap on an NFC tag-enabled product, rental item, parking meter, or other item with their iPhone, verify with Face ID, and complete the payment transaction. The news should provide a further incentive for product vendors and owners to incorporate NFC tags into their items, building on recent advancements in NFC tag production and the availability of very low-cost tags on the market.
Type Five NFC Tags that offer improved robustness, range, and greater compatibility with Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) readers will enable more reliable user experiences while allowing companies to track their supply chain more effectively. This will help to enable more compelling consumer engagement applications, better user experiences, and effective anti-counterfeiting and authentication use cases. In addition, many appliance manufacturers are beginning to adopt tags for brand protection purposes. For example, Philips has adopted NFC reader and NFC tag technology to authenticate toothbrush heads and configure device operation. ABI Research anticipates many more appliance vendors will integrate NFC reader technology into their devices to create a secure authenticated ecosystem for accessory authentication in the coming years.
Challenges and Recommendations |
RECOMMENDATIONS |
While NFC has seen strong growth in recent years, the technology has not yet reached its full potential. This still very much the early stages of NFC adoption beyond payments, and greater education of the technology for these alternative use cases is still very much required. According to a recent ABI Research survey on Consumer Attitudes, Experiences and Understanding of NFC, frequency of usage, user experience, confidence, and familiarity with NFC technology are all very positive, though more work needs to be done to ensure implementation issues to not degrade user experience, while greater education is needed around the unique capabilities of NFC technology and what it can bring to other use cases. In addition, ABI Research expects that post-COVID-19 the usage of contactless technologies will accelerate as a “contactless” or “touchless” experiences are demanded across multiple settings. While there has been a shorter-term boost towards enabling better hygiene and safety, ABI Research expects NFC to become more widely adopted outside of payments thanks to increased penetration of tags and contactless technology in a variety of these emerging use cases. The addition of wireless charging capabilities, improvements in user awareness via wayfinding marks, improved user experience via better performing and robust tags, better education and a growing reader installed base, alongside NFC being used alongside Bluetooth and Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) within secure ranging and provisioning applications will all help NFC build its presence in consumer and IoT markets over the next few years.