5G Digitally Transforms a Hunan Metal Foundry
|
NEWS
|
China Mobile and Huawei have deployed a private 5G network solution in the Hunan Valin Xiangtan Iron and Steel factory, which is one of the largest metal foundries in Hunan. The deployment includes more than 210 5G base stations and one Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) room ,which enables a multitude of use cases such as remote crane operations, smart robots, Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) inspections, 5G High-Definition (HD) video surveillance, and others.
One significant use case supporting remote crane operations through 5G. Using time-sensitive networking (TSN)-supported 5G systems that enable real-time programmable logic controller (PLC) connections, as well as 5G-connected video cameras on the cranes that transmit an HD stream of the factory floor in real time to the operator, operators can now remotely control their cranes collectively from a Network Operations Center (NOC).
Transformation Extends Beyond Business Outcomes
|
IMPACT
|
The above-mentioned use case exemplifies some of the positive social outcomes that can be derived from 5G enterprise deployments. In a traditional setting, a crane operator in a metal foundry would have to enter their crane ten stories above the factory floor in order to work. They have to navigate narrow stairs at a steep angle up 30 meters (98 feet), and then cross a narrow bridge to reach the crane operation room. The operator would work long hours in a hot, noisy, dusty, and isolated environment where vision of the ground situation was limited. However, digital transformation through 5G has allowed operators to remotely control cranes in an air-conditioned NOC. This has significantly improved the jobs of the crane workers. Now, multiple operators can remotely control their cranes in real time, with full visibility of the operations through seven HD cameras on each crane that transmit a continuous HD stream of the factory floor. This has improved collaboration and communication between crane workers, reduced health hazards and risks, and increased the overall quality of working standards. Furthermore, Hunan Valin Xiangtan Iron and Steel now has half of their crane operator workforce made up by women, whereas before the 5G enhancement, the factory had no female crane operators.
Beyond steel foundries, remote controlled cranes can also be deployed in ports and mines. Leveraging on eMBB, 5G can be paired with Artificial Intelligence (AI) for “intelligent” video applications. For example, using a 5G-enabled video surveillance camera in industrial scenarios can help identify and alert people from entering hazardous areas and recognize if workers are wearing a safety helmet. With 5G drones used for inspections, less people will have to perform the hazardous job of manually inspecting equipment in dangerous or hard to reach locations, such as natural gas pipelines, or oil and gas rigs.
Early Deployments into 5G will Reap Long-Term Benefits
|
RECOMMENDATIONS
|
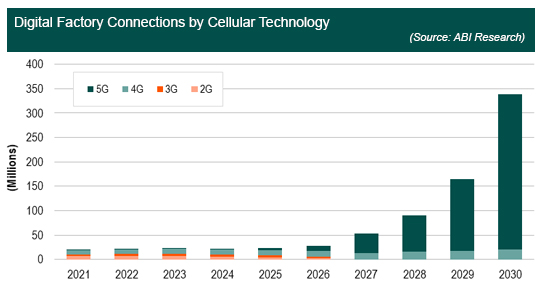
ABI Research anticipates that by 2030, there will be more than 317 million 5G connections globally on the factory floor. 5G connections on the factory floor will usher in a new age of digital transformation and become the leading form of cellular connectivity for factories come 2026 and is forecasted to see an explosion in growth beyond 2027. This is due to the maturity of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) standards, release of 5G-compliant devices, and an improved industrial ecosystem which will foster the development of more commercial use cases of 5G. The deployment of 5G does not only result in improved business outcomes and operational efficiencies, but has the potential to improve overall working conditions, digitize the workforce, and reduce occupational hazards.
Manufacturing executives should look towards adopting trialing 5G use cases as Proofs of Concept (PoC) before entering the mass adoption. Through such trials enterprise owners and executives can begin to fully understand how 5G should be deployed for their factories, and what are some of the business requirements and technical requirements. Companies hoping to deploy 5G should also understand some of the typical use cases that can be deployed in the factory or warehouse premises. This includes understanding some of the main features of 5G, such as gigabyte wireless connectivity and ultra-reliable low latency (URLLC). Through these features, 5G can enable enhanced production capabilities through technology such as Augmented Reality (AR) or Virtual Reality (VR) headsets to improve worker efficiency, especially in the maintenance and logistics domain, where having a heads-up display can reduce the time required to install or fix equipment. As 5G can meet some of the stringent data and low-latency requirements of AR and VR use cases, this would enable a mobile workforce to leverage these tools wirelessly. 5G can also increase the working efficiency of equipment and processes, such as through installing 5G-enabled Condition-Based Monitoring (CBM) modules in machinery or locations where wired CBM modules cannot reach. By leveraging 5G’s enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and URLCC capabilities to enable real-time streaming of important data into an AI model situated at the edge (e.g., MEC), fault prediction can be made more accurately, thus allowing for more cost-effective maintenance schedules, better pre-emptive rectifications, and lower downtimes for machinery and equipment.
