Neutral Host Providers Make a Noticeable Appearance on the Private Cellular Market
|
NEWS
|
As the value proposition for private cellular networks slowly but surely matures, it begins to attract interest from companies other than traditional infrastructure vendors, cellular Communication Service Providers (CSPs), and telecom system integrators. Particularly, tower companies like Cellnex, American Tower, AP Towers, Ascend Telecom, Indus, BSNL Tower, edotco, Vantage Tower, Crown Castle, SBA, and China Tower have recently advanced their neutral hosting activities to provide managed services for private cellular networks.
The concept of neutral hosting involves sharing infrastructure between multiple Mobile Network Operators (MNOs), enabling organizations to access high-speed, secure, and reliable wireless services without the need to build and maintain their own individual networks. This business model is attracting growing interest from enterprises of all sizes that are looking for cost-effective and efficient ways to meet their connectivity requirements. As the demand for private 5G networks continues to increase, neutral host providers are positioning themselves at the forefront of the industry, delivering cutting-edge solutions to organizations across the world.
Why are Open RAN Vendors More Successful in the Enterprise Domain?
|
IMPACT
|
Private cellular networks offer organizations greater control over their network infrastructure, improved network performance and security, and the ability to customize their network to meet specific needs. However, the deployment of private cellular networks can be complex, costly, and time-consuming, especially for organizations without the expertise or resources to manage their own networks.
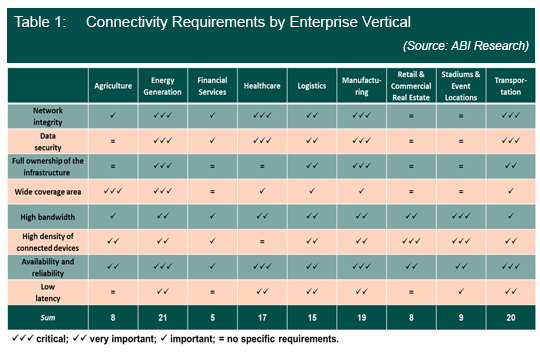
Neutral host providers offer a solution to this challenge by providing a turnkey solution for the deployment of private networks. This allows organizations to focus on their core business activities, secure in the knowledge that their network is being managed by experts. However, the enterprise opportunity is extremely fragmented as different verticals show different requirements, shown in Table One. While verticals like manufacturing and energy generation require full ownership of any communication infrastructure, verticals like retail, commercial real estate, or sports and hospitality venues are less interested in owning and managing their own network. At the same time, these verticals also tend to have tighter digitization budgets, which in turn increases the attractiveness of a private cellular network managed and operated by a neutral host.
More Agility and Economic Flexibility for Enterprise Offerings are Needed
|
RECOMMENDATIONS
|
While the success of neutral hosts in the private cellular market will certainly vary by vertical, their emergence will also a have more fundamental effects on the private cellular landscape in general.
First, neutral hosts can provide private cellular networks to enterprises in a more cost-effective and efficient manner than traditional MNOs as existing network infrastructure will be shared. This will increase competition in the market and drive down prices, making private 5G networks more accessible to a wider range of organizations.
Second, neutral hosts can have access to multiple MNOs, which allows them to provide more comprehensive network coverage and improve network resiliency. This will be especially important for organizations operating in remote locations or those with demanding network requirements. In addition, neutral hosts can work with enterprises to tailor private 5G networks to their specific requirements, such as network capacity, performance, and security. This level of customization will be especially important for organizations with highly specialized network requirements.
Third, neutral hosts can drive innovation in the private 5G market by providing new and innovative services and capabilities. This can extend to aspects like network slicing, which will allow organizations to create customized, dedicated networks for specific applications and use cases. By providing access to multiple CSPs, neutral hosts can furthermore reduce the risk of vendor lock-in for enterprises. This will allow organizations to choose the best CSPs for their specific needs and negotiate more favorable terms.
To prepare for these developments, established actors within the telecom industry should react to the emergence of neutral hosts and private 5G to remain relevant and/or, in some cases, even competitive. In addition to embracing the neutral host providers and engage in partnerships with them (see IN-6792 for a more thorough discussion), companies should:
- Offer End-to-End Solutions: As the business model of neutral host providers relies on easy scalability (i.e., renting the same communication network to a range of different tenants), infrastructure vendors and System Integrators (SIs) should focus on designing modularized and easily scalable connectivity solutions for building, deploying, and maintaining 5G networks for neutral hosts, including hardware, software, and services.
- Focus on Network Security: With the increasing demand for private 5G networks, telecoms must ensure the security of their networks to protect against cyber-attacks. This becomes particularly important in a neutral host scenario, as networking infrastructure will inevitably be shared between different tenants/end-users. Therefore, all partners involved will need to ensure that appropriate cybersecurity measures are implemented to ensure the safety of the overall network as well as the integrity of each individual tenants’ data.
- Invest in Research and Development: Investing in research and development can help telecoms stay ahead of the curve and offer innovative solutions to the market.
- Stay Updated on Industry Trends: Keeping up-to-date with industry trends and new technologies is crucial for telecoms to remain competitive and meet the needs of neutral hosts and their customers.
-

