The modern enterprise only uses about 5% of the data it generates. With so much vital information flying under the radar, companies are not always making the best business decisions. This challenge will only worsen if you do not adopt a data fabric.
As defined by ABI Research in a recent blog post, an enterprise data fabric is “an integration architecture that unifies data collected from various business units.” In other words, the data fabric serves as a central platform connecting data across departments and regions. This ensures stakeholders have a window into adjacent operations to accelerate decision-making capabilities.
With industries becoming more digitally-driven, enterprises are generating more data than ever before. The massive surge in data generation highlights the need for more advanced data management tools—like data fabrics—to handle and streamline this influx of information. ABI Research projects enterprises to spend 3X as much on data fabric solutions by 2030, primarily fueled by data storage and data integration applications.
The Growing Challenge of Managing Data
Enterprise data generation is only growing with every passing year. For example, our analysts expect industrial firms to produce a staggering 4.4 Zettabytes (ZB) of data annually by 2030—more than double the amount of data generated in 2023. This rapid growth of data makes it more challenging for enterprises to organize and make sense of data from a wide range of sources.
For industries like manufacturing and automotive, managing the vast amounts of information coming from sensors, machines, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices is becoming an increasingly complex task. Without proper data management frameworks, enterprises risk inefficiencies, information overload, and missed opportunities.
Data Silos Are a Significant Obstacle
One of the primary issues holding back enterprises from realizing their full potential is the presence of data silos. These isolated pools of data are created when information is stored separately across different departments or platforms, preventing it from being accessible or shared across the organization.
According to a survey of manufacturers by ABI Research, 25% identified data silos as a major hurdle to their digitization efforts. Without a way to seamlessly integrate these data, companies lose valuable insights and struggle with slow decision-making.
Chart 1: Please rank from 1 to 3 (where 1 is an urgent priority) which of the following are a challenge to your business or operations today?
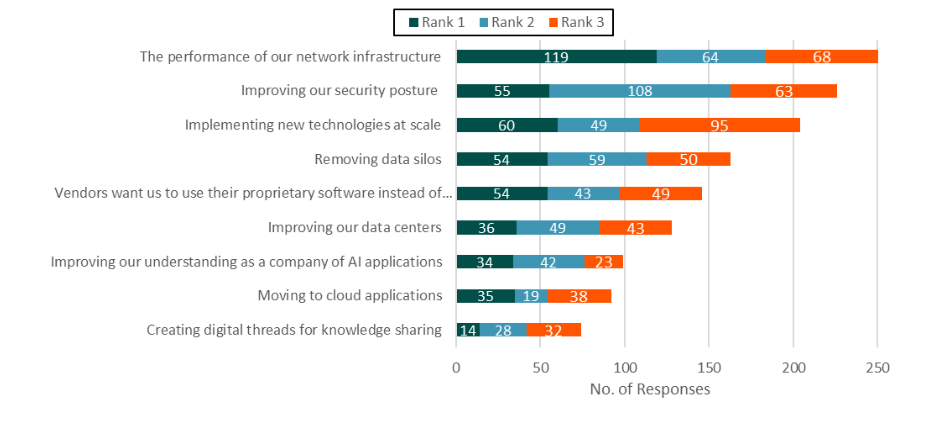
(Source: ABI Research)
Our multi-client survey also revealed that manufacturers possess the necessary tools for data, but lack the workforce culture and the capabilities to turn their data into actual business use cases.
Chart 2: Manufacturers’ Survey Responses About Their Data Competencies
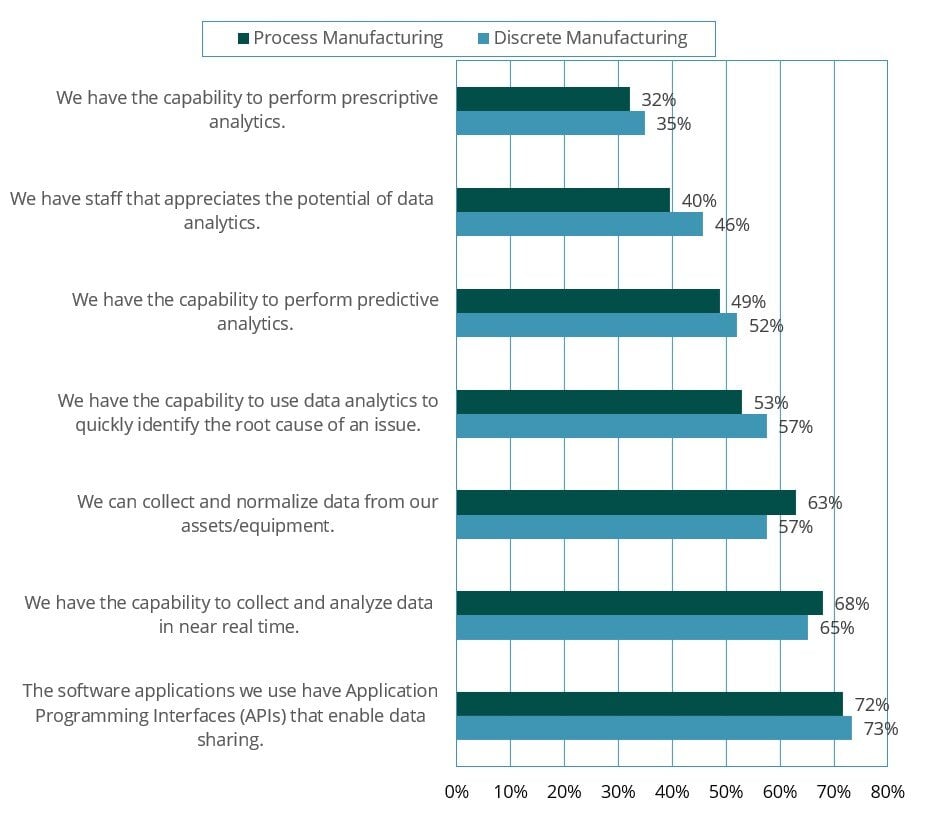
(Source: ABI Research)
Data fabrics offer a solution to this problem by integrating data from multiple sources and providing a unified view of all the information flowing across the organization. By breaking down silos, enterprises can access real-time data across different business functions, enabling faster, more informed decision-making.
Economic Drivers Behind Data Fabric Adoption
Several economic factors are also driving the need for enterprise data fabrics:
- Quality Enhancements: A unified data framework allows for more accurate analytics, leading to improved quality of decision-making and process outcomes. In manufacturing, this results in better products, while in services, it leads to an enhanced user experience.
- Greater Efficiency: By automating data integration, data fabrics streamline processes, eliminating the need for manual data entry or reconciliation. This reduces the time and resources required to gather, share, cleanse, and prepare data for use. The end result is data being fed to the right people at the right time.
- Maximizing Data Utilization: Data generation is not cost-free. With rising energy prices and the increasing demand for data centers, enterprises need to justify the resources spent on generating and storing data. Data fabrics enable companies to make better use of their data by harmonizing and normalizing it for further analysis.
Related Content:
- Integrating Enterprise Data With A Hybrid Cloud Approach
- Key Insights from IMTS: Recommendations for Data Fabric Vendors to Win Over Industrial Enterprises
- Make Data Integration Exciting Again: Data Fabric Announcements at Microsoft’s Build 2024 Tries to Tie Technology to Use Cases, Providing Important Lessons for the Industry
Benefits of Data Fabrics
Data fabrics offer a wide range of benefits that make them a key tool for modern enterprises:
- Unified Data Management: By integrating data from multiple sources, data fabrics eliminate silos and provide a comprehensive view of enterprise data. For example, beauty brand L’Oréal centralizes financial data, systems, processes, and analytics across various departments and countries to facilitate a robust data sharing strategy.
- Scalability: As data volumes grow, data fabrics can scale to handle more data, ensuring that businesses can continue to operate efficiently.
- Faster Decision-Making: With access to real-time, harmonized data, enterprises can make faster, better-informed decisions.
- Enhanced AI and ML: Data fabrics provide the high-quality, structured data needed to train Artificial Intelligence (AI) models and drive Machine Learning (ML) applications.
- Cost Efficiency: By automating data management and eliminating redundancies, data fabrics help enterprises lower operational costs, while improving service levels.
Data Fabric Use Cases
Data fabrics are not just a solution for managing enterprise data—they also open the door to a wide range of innovative applications. Below are several key use cases where data fabrics can make a significant impact.
1. Facilitating AI and ML
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are highly dependent on large datasets to train models and improve their effectiveness. Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT-3, rely on vast amounts of data for training. However, enterprise data are far more diverse and complex than the simple text data typically used in these models. Data fabrics help aggregate and organize this complex data, making it easier for AI systems to learn and generate actionable insights.
Example: Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance is a vital use case for AI in industries like manufacturing. Data fabrics allow companies to gather and integrate data from sensors, machines, and historical performance records. This enables AI models to predict when equipment is likely to fail. In turn, businesses can plan maintenance proactively, which provides time and cost savings, avoidance of downtime, and extended asset life span.
2. Real-Time Analytics for Decision-Making
Data fabrics allow enterprises to access harmonized data in real time, enabling faster decision-making and more agile responses to changing business conditions. Whether it's in logistics, retail, or manufacturing, real-time data are essential for keeping operations running smoothly. Companies like Unilever and Shell are already leveraging data fabrics for cross-department data sharing/collaboration.
Example: Retail Inventory Optimization
In retail, maintaining the right stock levels is critical. Data fabrics enable retailers to combine data from point-of-sale systems, supply chain platforms, and customer behavior analytics to make data-driven decisions about restocking. This real-time view of inventory helps businesses optimize their operations and better meet customer demand.
3. Streamlining Industry 4.0 Operations
As companies adopt Industry 4.0 technologies, they need to manage increasingly complex data streams from connected devices and systems. A data fabric solution can unify these streams, enabling enterprises to run more efficient and scalable operations.
Example: Smart Manufacturing
In a smart manufacturing setup, machines and systems produce a continuous flow of data. Data fabrics allow manufacturers to integrate data from sensors, production lines, and other connected equipment into a single, cohesive framework. This helps manufacturers monitor their entire operation, optimize production, and ensure better quality control.
4. Enhanced Data Security and Compliance
Data security is a top priority for enterprises handling sensitive or regulated information. Data fabrics help ensure data remain secure by providing consistent security protocols across different systems. They also help companies meet regulatory requirements by giving them better control over data access and usage.
Example: Financial Services
In the financial sector, maintaining data security and regulatory compliance is essential. Data fabrics allow financial institutions to integrate data from multiple sources, ensuring secure access, while complying with regulations. With this technology, financial institutions can make better use of their data without compromising security.
Conclusion
The adoption of data fabrics is rapidly becoming a necessity for enterprises across various industries. As the volume of data continues to grow, and as new technologies like AI and the IoT become ubiquitous, the need for efficient data management solutions will only become more apparent. Data fabrics offer the scalability, flexibility, and security that modern enterprises need to stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world.
Learn more about how data fabrics can benefit your organization, their growth drivers, and the companies offering solutions by checking out ABI Research’s Hybrid Cloud & 5G Markets Research Service.
About the Author
 Leo Gergs, Principal Analyst
Leo Gergs, Principal Analyst
Leo Gergs leads the research in 5G Markets, including 5G monetization models. While this also includes success stories in the consumer domain, his research focuses on cellular revenue opportunities for enterprise connectivity. Within this context, he leads ABI Research’s work on private cellular networks and the role of hyperscalers, infrastructure vendors, Communication Service Providers (CSPs), and System Integrators (SIs) for enterprise connectivity.


