5G Massive Multiple Input, Multiple Output (mMIMO) is one of the biggest breakthroughs in wireless communications. It broadens mobile network coverage, expands data capacity, and provides a top-tier user experience for mobile users. Massive MIMO is quickly becoming a staple in the telecommunications industry, with ABI Research forecasting just shy of 47 million radio shipments annually by 2027.
What Is 5G Massive MIMO?
5G massive MIMO is a wireless hardware technology that enables superior 5G connectivity by using transceivers and receiver chains of more than eight streams. By using multiple antennas, mobile operators can widen cellular coverage areas and increase data capacity and user throughput. Spatial multiplexing, beamforming, and other novel solutions with massive MIMO can be deployed at the radio, in the baseband, or in both locations. The deployment flexibility afforded by MIMO translates into expanding signals in specific directions, which allows for high beamforming gain.
What Technologies Form Massive MIMO?
The following technologies are integral to making massive MIMO capabilities possible.
Spatial Multiplexing
Through spatial multiplexing, massive MIMO allows for multiple data streams to be on the same time-frequency symbol, also known as spectrum reuse. Users can either receive multiple data streams on a single device or spread it out among multiple devices. Moreover, wireless systems using massive MIMO have higher data rates and network capacity via array gain and spatial multiplexing.
Beamforming
Beamforming amplifies signals in certain directions, creating a narrow, high-gain beam toward an end-user device. This advanced MIMO technology improves the radio link for target devices, which results in a better Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR). Consequently, the telco radio link will have a superior level of network coverage, capacity, and user throughput.
Open RAN
Complex telco technologies like massive MIMO require standardization and deployment flexibility. Open Radio Access Networks (RANs) meet this demand, as they sport a modular approach to 5G connectivity. With Open RAN, operators don’t have to worry so much about which equipment vendor to choose. Open RAN aims to decouple hardware from software, thereby introducing improved vendor interoperability. This open nature to cellular connectivity is in stark contrast to traditional RAN, which typically involves vendor lock-in.
Take a deep dive into the technologies enabling 5G mMIMO by downloading ABI Research’s 5G Massive MIMO Market Developments technology analysis report.
How Cellular Networks Benefit from 5G Massive MIMO
The business case for massive MIMO is to achieve connectivity benefits that outweigh traditional MIMO systems. Below is a list of various use cases where 5G massive MIMO has an advantage over legacy MIMO.
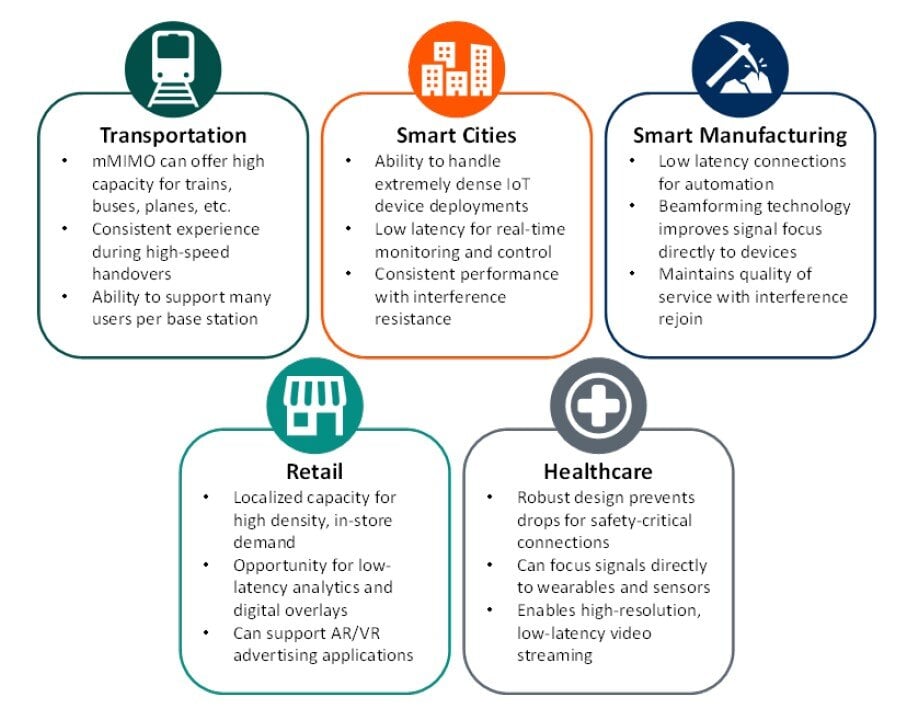
- Transportation: In transportation contexts, massive MIMO provides high capacity for trains, buses, planes, and other public transport systems. Massive MIMO is also key to supporting numerous users simultaneously per base station and facilitating a consistent user experience.
- Smart Cities: Smart city applications often involve significantly dense Internet of Things (IoT) device deployments, which require low latency for real-time monitoring/control and consistent performance. 5G massive MIMO is a suitable option for these use cases, given its robust connectivity features.
- Smart Manufacturing: 5G massive MIMO supports industrial automation through low-latency connections. The beamforming technology is also a huge benefit for manufacturers because it provides a superior signal focus for connected devices.
- Retail: For retailers, massive MIMO can serve as the connectivity backbone for localized capacity for high density, in-store 5G demand, low-latency analytics and digital overlays, and Augmented Reality (AR)/Virtual Reality (VR) advertising applications.
- Healthcare: Hospital workers and other healthcare professionals will benefit from massive MIMO's robust designs for safety-critical connections, stronger radio links to wearables and sensors, and high-resolution, low-latency video streaming.
Figure 1: Use Cases of 5G Massive MIMO
(Source: ABI Research)
Massive MIMO Faces Massive Challenges
Massive MIMO has established itself as an essential technology for mobile networks and that trend will only become more apparent through the decade. In that period, technological innovations will increasingly embed themselves within the massive MIMO market. Examples include software-based Open RAN, Huawei’s Extremely Large Antenna Array (ELAA), new generation chipsets, and gallium nitride-based power amplifiers, among others.
As the telecommunications industry further progresses toward 5G MIMO, ABI Research foresees three key challenges to tackle:
- Fronthaul Specifications: Ongoing debates about spec proposals from vendors must be settled as the O-RAN Alliance approaches its finalization of fronthaul specifications enabling advanced massive MIMO capabilities. Settling these debates is integral to facilitating interoperability between multiple network equipment vendors.
- Energy Efficiency: Open RAN-based massive MIMO still has power consumption levels comparable to traditional RAN massive MIMO. To reduce carbon footprints and minimize Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), the former needs improved energy efficiency. This can be achieved through virtualization, optimized Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML) software, and the potential adoption of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) to replace Central Processing Units (CPUs).
- Performance Gap: Traditional RAN massive MIMO currently has a performance ceiling due to the nature of proprietary solutions from vendors. It is, therefore, crucial that vendors avoid creating this bottleneck with 5G Open RAN by developing a vendor-agnostic ecosystem.
This content is part of our 5G, 6G & Open RAN Research Service. A subscription to the service provides you with qualified and quantified analyses of the various technologies, trends, and vendors shaping indoor and outdoor mobile network deployments. If you’d like to learn more about this opportunity, speak to a member of our sales team.


