Automation is bound to serve a crucial cellular network function in the face of increased enterprise digitization. The accelerated demand for connectivity, in tandem with more data generated on enterprise premises, makes the manual configuration of cellular networks inadequate. Network automation is important for optimizing limited radio resources in an age when 5G technology introduces more complicated network management.
What Is Network Automation?
Network automation refers to the automation of manual tasks and processes involved in enterprise network management, such as security compliance, data analysis, network mapping, and network updates. Consequently, automation software provides Information Technology (IT) teams with greater speed and consistency, while saving the enterprise time and money.
Automation software, leveraging programmable logic, can automate network configuration and manage, test, deploy, and operate physical and virtual devices within a network. Repetitive network tasks, functions, and processes are controlled and managed automatically. As a result, this improves network service availability and minimizes labor needs.
Benefits of Network Automation
The main benefit of network automation is that it's effective at giving network management duties back to the enterprise. One thing that's important to remember is that end-market enterprises, such as manufacturers and warehouse operators, have their own order of priorities that often exclude network management. For example, a factory manager is primarily concerned with the quality of manufactured goods. Or a shipping port operator cares mainly about the quality and frequency of loading operations.
As you can see, managing cellular network architecture is low on the list of priorities for enterprises. Historically, this has resulted in enterprises outsourcing network management and operational capabilities to telco experts, such as Communication Service Providers (CSPs). However, automation changes the game. With automation software, the manufacturer or the shipping port operator can manage and operate their cellular connectivity without third-party involvement by using what is often called a Self-Organizing Network (SON).
Automating the Core Network
The core 5G network, the heart of cellular network architecture, is the first important part of the network that can be automated. The core network is responsible for the following functions:
- Reliable, secure connectivity to network end users
- Providing access to its services
- Taking care of essential cellular network functions like connectivity and mobility management, authentication and authorization, and subscriber data and policy management
But the problem is that, to enterprises, handling these network functions is the most challenging aspect of network management.
Core network functions are seen as very telco centric and too sophisticated to manage without in-house expertise. Acquiring these skills is a time-consuming and high-cost endeavor. While large multinational corporations can summon the resources to gain core network function expertise, the larger Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) community will see little value in doing so.
From here, SMEs can either strike partnerships with telco specialists or turn to non-cellular connectivity technologies. On that account, automating the 5G core network and its functions will be a crucial enabler of enterprise cellular and private networks, significantly reducing the complexity for enterprises.
Just be mindful that if full core network automation is to come to fruition, the 5G network will need to be completely cloud native. A cloud-native network requires both User Plane (UP) and Control Plane (CP) functions to occur in the cloud.
Automating the Radio Access Network (RAN)
Another important element of the network architecture that can be automated is the Radio Access Network (RAN), a cellular technology gaining further traction in the Asia-Pacific region. RAN automation and intelligent RAN control, supported by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), can make network management more straightforward and allow network operators to use limited radio resources more efficiently.
Traditional RAN automation, developed by a team of engineers through mathematical modeling and equations, is somewhat limited for today's applications. It can't provide fully closed loop automation, isn't well-suited for scalable connectivity, and is based on human observations. This backward-looking approach to RAN automation is being replaced with new AI/ML technological solutions.
AI/ML-assisted automation systems can teach ML models to apply a set of RAN predictions, actions, and policies for improving network performance. The system does this by automatically abstracting data from the RAN infrastructure. As a result of this AI/ML-assisted automation system, network operators, such as CSPs, Systems Integrators (SIs), and network departments within an enterprise, are no longer burdened with the need to adjust RAN parameters. Ultimately, this reduces human error and network downtime, while reducing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
From the enterprise's perspective, bolstering production and increasing revenue are the most important concerns, not managing a 5G network. This means they want a network management solution that can improve efficiency in the most simplified way possible. With the help of AI/ML software, RAN automation, and intelligent RAN control can do just that by bringing about more efficient network flows and revenue streams. Additionally, the AI/ML automation system addresses the growing commands of data analysis.
It's important to note that for AI/ML-enabled RAN automation to mature, key cellular players must get more actively involved. This means standardization bodies, network operators, hardware and software vendors, SIs, and hyperscalers must often test and verify the solution. Through rigorous testing, AI/ML-assisted RAN automation solutions will be more trustworthy, and a centralized strategy can be developed for large-scale deployments.
Figure 1: Advantages of AI/ML-Driven RAN Automation
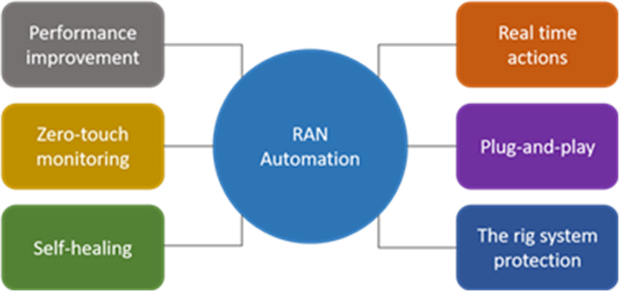
Conclusion
Network automation is synonymous with a new generation of telco infrastructure. In combination with network disaggregation and network virtualization, these three important trends will define enterprise cellular infrastructure for the foreseeable future. To learn more about the latest network architecture trends and implications on the supply and value chain for enterprise cellular connectivity, download ABI Research’s Infrastructure Vendor Strategies for Enterprise Cellular research report—part of the company’s 5G Markets Research Service. This report also has a section that will help implement automated solutions within a cellular network.
Related Content:
Why Are Open RAN Vendors Emerging as Potent Partners for Enterprise Cellular? [Insight]
Open RAN Standards Could Unlock Private Cellular Network’s Commercial Value [Insight]
6G: The Network of Technology Convergence [Whitepaper]
The Promising Outlook for 5G [Infographic]
